Tooth illness is a broad term that encompasses any condition affecting the teeth, gums, or surrounding structures. This includes common ailments such as tooth decay, gum disease, tooth sensitivity, and others that can significantly impact a person’s oral health. Oral health is integral to overall wellbeing, and neglecting it can lead to various complications, including severe discomfort, infections, and even systemic diseases. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of tooth illness, explore its various types, causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and treatments.

What are Tooth Illnesses?
Tooth illnesses refer to a wide range of conditions that affect the oral cavity, particularly the teeth and gums. These conditions can stem from various factors, including poor hygiene, diet, lifestyle choices, and underlying health issues. Understanding these illnesses allows us to intervene early and maintain optimal oral health.
The impact of oral health on overall health is profound. Research has shown that poor oral hygiene can contribute to serious health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Conditions like tooth disease and gum diseases can harbor bacteria that may enter the bloodstream, leading to inflammation and other complications elsewhere in the body.

This article aims to cover several main types of tooth illnesses, including tooth decay, gum disease, and more. By comprehending these conditions, we empower ourselves to take proactive steps to improve our dental health.
The Importance of Oral Health
Oral health is often overlooked, but it deserves significant attention. Healthy teeth and gums not only enhance one’s smile but also contribute to effective nutrition and overall health.
Neglecting oral hygiene can lead to a cascade of problems. For instance, chronic gum disease can result in painful chewing, nutritional deficiencies, and even speech difficulties. This emphasizes the need for regular dental checkups and a solid daily oral hygiene routine.
Types of Tooth Illnesses
In the following sections, we will explore various types of tooth disease in humans. Each type presents unique challenges and requires specific care and management approaches. From common teeth problems like decay to complex teeth disorders, understanding each condition is key to maintaining excellent oral health.
Tooth Decay (Dental Caries)
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is one of the most prevalent forms of tooth illness. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities and eventually more severe dental issues if left untreated.
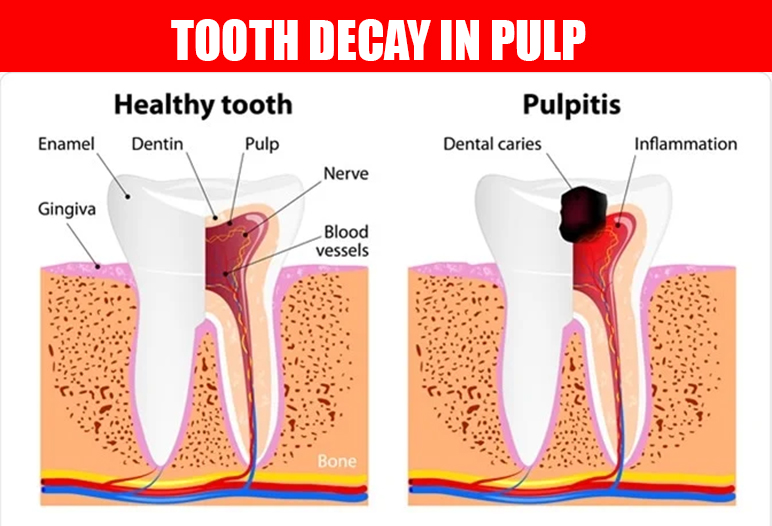
The Process of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay begins with the formation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the surface of teeth. When we consume sugary foods or drinks, the bacteria feed on the sugars and produce acids. Over time, these acids wear down enamel, creating small holes or cavities in the teeth.
As the decay progresses, it can penetrate deeper into the tooth structure, reaching the pulp where nerves and blood vessels are located. This can cause significant pain and may require more invasive treatments, such as root canals, if not addressed promptly.
Risk Factors for Tooth Decay
Several factors can increase the risk of developing tooth decay:
- Diet: A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates provides food for bacteria, promoting acid production.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up and strengthen its hold on teeth.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids, so reduced saliva flow can exacerbate decay.
Understanding these risks is crucial in preventing tooth decay. Adopting healthier dietary habits and maintaining good oral hygiene practices can significantly lower the chances of developing this condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Recognizing the signs of tooth decay early is essential for effective treatment. Symptoms may include:
- Cavities: Visible holes or dark spots on teeth indicate advanced decay.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet substances may signal underlying decay.
- Pain: Persistent toothache or discomfort can indicate damage to the tooth’s structure.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a dentist as soon as possible.
Importance of Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is your first line of defense against tooth disease. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help keep plaque at bay.
Moreover, regular dental checkups are imperative. Dentists can spot early signs of decay that you might overlook, allowing for timely intervention. Professional cleanings remove tartar buildup and contribute to a healthier oral environment.
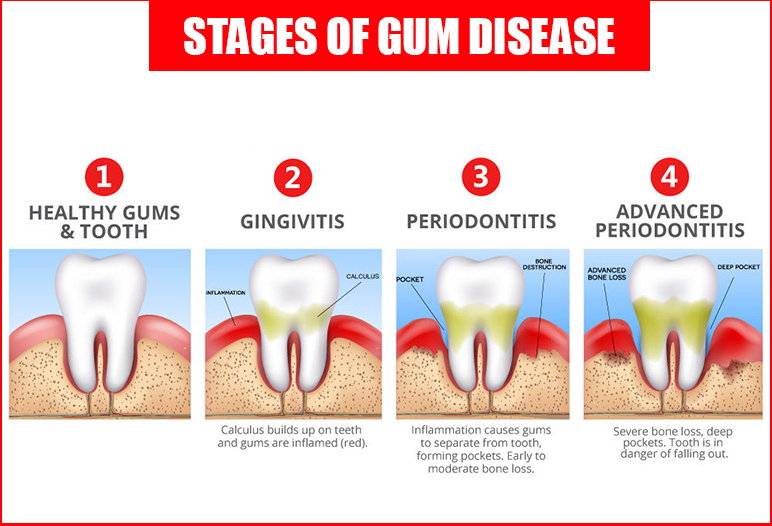
Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is another prominent tooth illness that affects millions of people worldwide. It begins as gingivitis and can progress to more severe forms if not treated adequately.
Stages of Gum Disease
There are two primary stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: This initial stage is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. Gingivitis is often reversible with improved oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the inflammation extends below the gum line. This can lead to loss of supporting bone and tissue around teeth, potentially resulting in tooth mobility and loss.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Various factors can contribute to the development of gum disease, including:
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk and severity of gum disease.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes makes individuals more susceptible to infections, including gum disease.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can reduce saliva flow, increasing the risk of gum disease.
By being aware of these risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their risks.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Signs of gum disease may include:
- Red, Swollen Gums: Inflamed gums indicate irritation and infection.
- Bleeding: Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing are a warning sign of gum disease.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath can be a result of bacterial buildup and gum disease.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek dental advice to prevent progression.
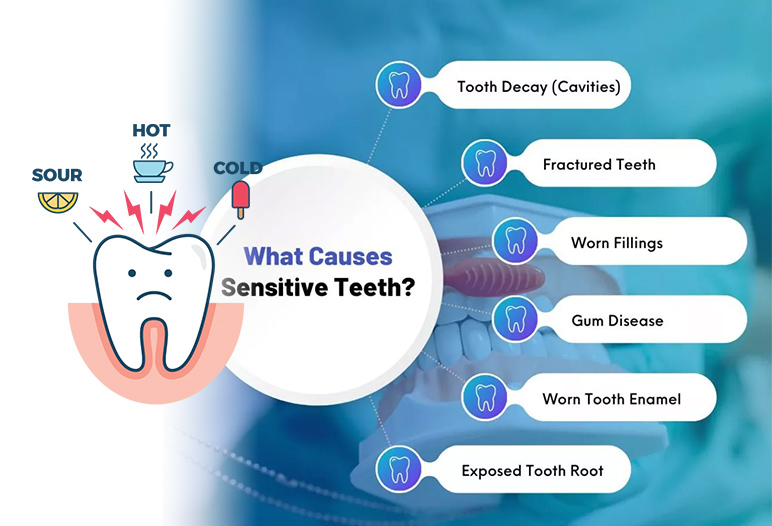
Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common complaint among many individuals and can be associated with various teeth disorders. It occurs when the underlying dentin becomes exposed, leading to discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
Several factors can contribute to tooth sensitivity:
- Exposed Dentin: Receding gums may expose the softer layer of the tooth, making it more sensitive to stimuli.
- Cracked Teeth: Cracks can create pathways for temperature changes and sensations to reach the nerve endings inside the tooth.
- Grinding Teeth: Excessive grinding can wear down enamel and lead to increased sensitivity.
Identifying the underlying cause is key to finding appropriate relief.
Treatment Options for Tooth Sensitivity
Fortunately, there are several treatment options for managing tooth sensitivity:
- Desensitizing Toothpaste: Specialized toothpaste can block the transmission of sensation from the tooth surface to the nerve.
- Fluoride Treatments: Professional fluoride applications can help strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
- Dental Procedures: For severe cases, dentists may recommend procedures such as bonding or crowns to protect exposed areas.
Addressing sensitivity early ensures that it does not interfere with daily life and helps maintain a positive quality of life.
Tooth Erosion
Tooth erosion is another concerning issue that can lead to tooth disease. It involves the loss of tooth enamel due to exposure to acids, whether from diet or medical conditions.
Causes of Tooth Erosion
Common causes of tooth erosion include:
- Acidic Foods and Drinks: Citrus fruits, soda, and wine have high acid levels that can erode enamel over time.
- Acid Reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) exposes teeth to stomach acids, accelerating erosion.
By understanding these causes, individuals can make better dietary choices and seek medical advice for conditions like GERD.
Preventive Measures for Tooth Erosion
Preventing tooth erosion involves several strategies:
- Limiting Acidic Beverages: Reducing the consumption of sodas and citrus juices can help protect enamel.
- Using a Straw: When drinking acidic beverages, using a straw can minimize contact with teeth.
- Rinsing with Water: After consuming acidic foods or drinks, rinse your mouth with water to help neutralize acids.
Educating yourself about preventive measures can go a long way in safeguarding your teeth from erosion.
Cracked Teeth
Cracked teeth are another common issue that can arise from various activities or habits. They can lead to significant discomfort and may require professional intervention.
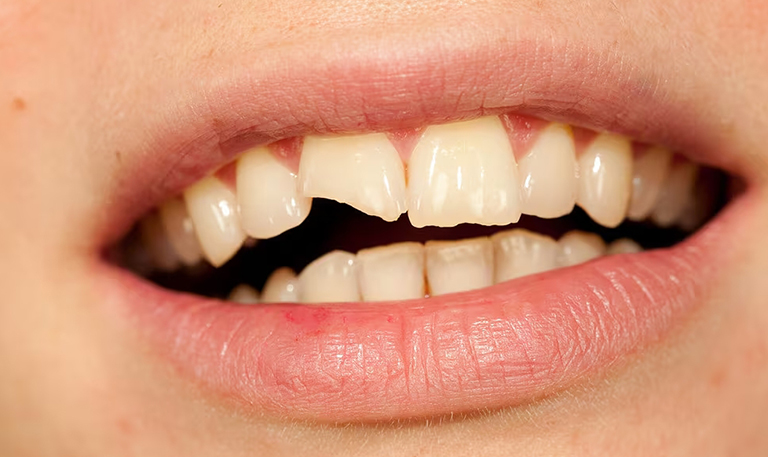
Causes of Cracked Teeth
Several factors can lead to cracked teeth, including:
- Trauma: Accidents or falls can result in cracks.
- Biting Down Hard: Chewing on hard objects, such as ice or hard candy, can stress teeth beyond their capacity.
- Grinding Teeth: Habitual grinding can weaken teeth and lead to cracks.
Being cautious with your habits is crucial in preventing cracks from occurring.
Treatment Options for Cracked Teeth
Treatment for cracked teeth typically involves:
- Dental Bonding: Minor cracks may be repaired with dental bonding materials.
- Crowns: More severe cracks may require the placement of a crown to restore functionality and protect the tooth.
Seeking prompt dental care for cracked teeth can prevent further complications and alleviate discomfort.
Diseases that Cause Tooth Loss
Tooth loss can be a distressing outcome of various tooth illnesses. Understanding the diseases that cause tooth loss is essential for prevention and management.
Periodontitis
Severe gum disease, or periodontitis, is a leading cause of tooth loss. Inflammation and infection can destroy the supporting structures of teeth, leading to mobility and extraction if untreated.
Early intervention through proper oral hygiene and professional care can help prevent the progression of periodontitis.
Diabetes
Diabetes has a well-established link to oral health issues, particularly gum disease. Elevated blood sugar levels can impair healing and increase susceptibility to infections, leading to tooth loss.
Managing diabetes effectively through diet and medication can mitigate these risks and safeguard oral health.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can weaken the jawbone, making it less capable of supporting teeth. As the bone density decreases, teeth may become loose and susceptible to loss.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including weight-bearing exercises and adequate calcium intake, can help support bone health.
Conclusion
Tooth illness encompasses a wide range of conditions that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. From tooth decay to gum disease, understanding these issues is vital for effective prevention and management. Adopting good oral hygiene practices, being mindful of dietary choices, and seeking regular dental care are essential steps in maintaining optimal oral health.
Empowering ourselves with knowledge about common teeth problems and their solutions enables us to take an active role in our health journey. Whether you’re asking, “How do I stop tooth decay?” or seeking ways to manage gum disease on one tooth, remember that proactive measures can make all the difference. By prioritizing oral health, we pave the way for a healthier, happier future.



SAIGON CENTER DENTAL CLINIC
Best dentist in Vietnam
Saigon Center Dental Clinic is proud to be one of the most prestigious dental clinics in Ho Chi Minh City with a variety of services: Single dental implant, Full jaw dental implant (especially All On 4, All on 6, and Zygoma Implant), Cosmetic porcelain crowns, Porcelain veneers, Braces, Clear braces, Tooth fillings, Wisdom tooth extraction, Treatment of toothache...
SAIGON DENTAL IMPLANTS CENTER
Best dentist in Vietnam
Saigon Implant Center - Dental Clinic utilizes the latest technology for specialized treatment in the field of Single implant, full jaw implants, All on 4 implants, All on 6 implants, Zygoma implant....